Rancidity in oils pdf
Data: 2.09.2018 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 990Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Rancidity in oils pdf
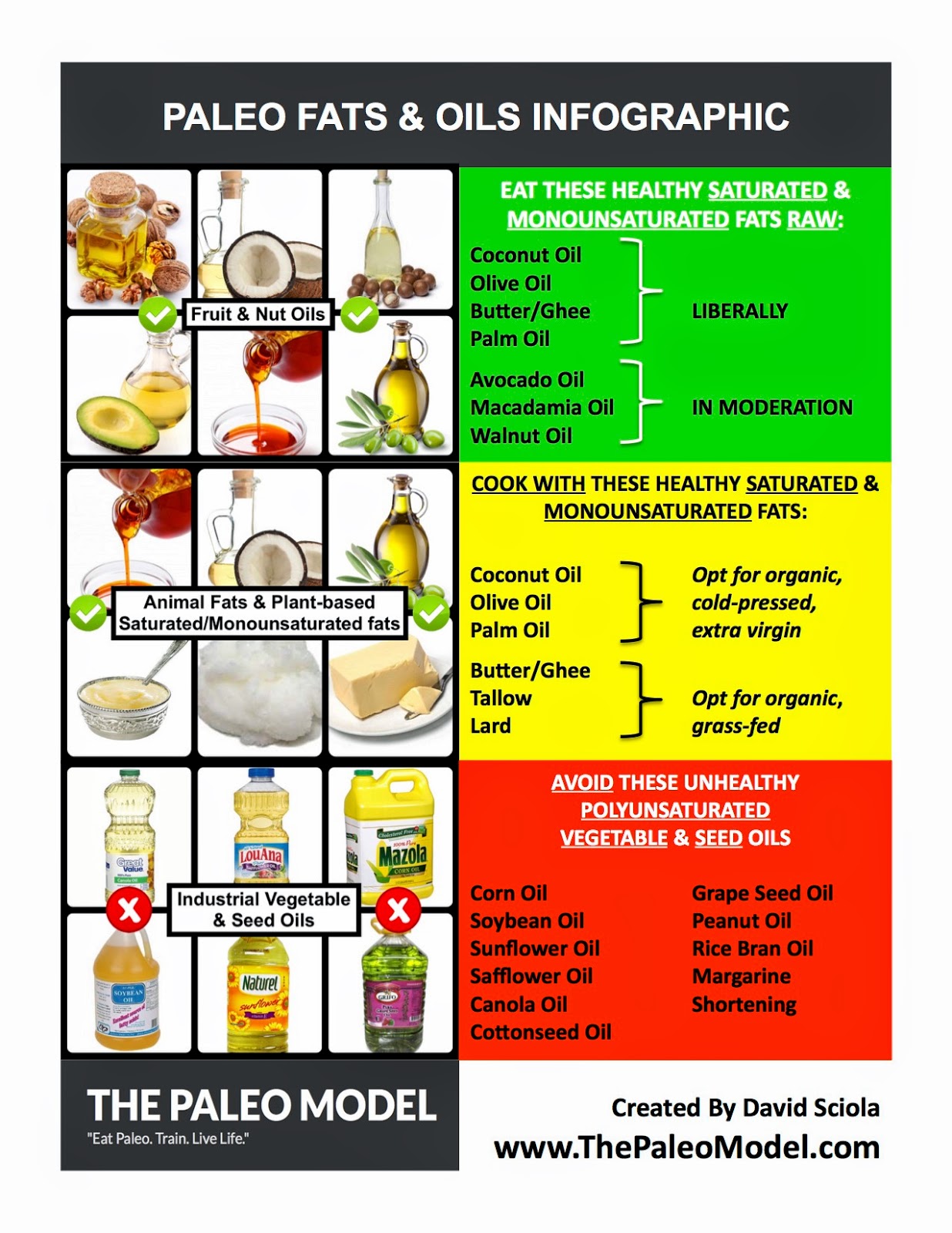
Rancidity is one of the major problems in relation with use of vegetable oils. Time, temperature, light, air, exposed surface, moisture, nitrogenous organic material, and traces of metals are known to be factors responsible for rancidity. The principal danger is the occurrence of rancidity, since nuts are composed mainly of fats. Fats are carboxyl compounds made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and make up one of the principal Fats containing unsaturated fatty acids are always liquid (oils) at room temperature. Their melting point is lower than saturated fats. Heat Request PDF on ResearchGate On Mar 17, 2008, Fereidoon Shahidi and others published Methods of Measuring Oxidative Rancidity in Fats and Oils For full functionality of ResearchGate it is. Vegetable Oils Soybean, palm oil, rapeseedcanola, sunflower, cottonseed, peanut, sesame, corn, olive, coconut, cocoa butter etc. Hydrolytic rancidity refers to the rancidity that occurs under conditions of moisture, high temperature, and natural lipolytic enzymes. The Rancidity is a term generally used to denote a condition of unpleasant odours and flavours in foods resulting from deterioration in the fat or oil portion of a food. RANCIDITY HYDROLYTIC RANCIDITY OXIDATIVE RANCIDITY MICROBIAL RANCIDITY Download Measuring Rancidity in Fats and Oils. Share Embed Measuring Rancidity in Fats and Oils Please copy and paste this embed script to where you want to embed RANCIDITY The term rancid is used to describe either objectionable odours or tastes in many food products. Galliard DSc, FRSC, FIFST outline the causes, methods of measurement and ways of preventing rancidity in foods. Rancidity Of Oils And Fats Pdf. 0 Comments \n Understanding Rancidity of Nutritional Lipids. Since ancient times, deterioration of lipids has been a major problem in the storage of oils and fats. Often referred to as rancidity, it is the natural process of decomposition (degradation) of fats or oils by either hydrolysis or oxidation. A Study of Rancidity of Olive Oils S. KALOYEREAS Louisin State University, Baton Rouge, Louisiana I NVESTIGATION of the problem of rancidity is rendered difficult by the fact that the ultimate standards to which all data must be referred are based on taste and smell. RANCIDITY CONTROL OF WATERBASED METALWORKING FLUIDS. Rancidity is one metalworking fluid problem which demands immediate attention. Employees will not tolerate a foul smelling fluid and even if they would, the rust, loss of finish, poor tool life, and the generally poor metalworking fluid performance that accompany rancidity are major problems in metalworking operations. Chemistry of Oils and Fats All oils contain a proportion of all three types and it is this combination in any are relatively stable to oxidation and the development of rancidity and are now considered, in nutritional terms, as being the best type of fat to eat. 4 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2. 1 OXIDATION AND RANCIDITY OF FATS AND OILS Lipid oxidation is one of the major reasons that foods deteriorate and is caused by the Peroxide Value test in Fats and Oils With the analysis systems in CDR FoodLab range, in just 4 minutes, without titration, using micro quantity of sample you can carry out the Peroxide Value test of edible Oils and fats like Olive oil, Nuts oil, Walnut oil, Peanut oil, Sunflower oil, castor oil, Palm oil and the other vegetable oils. Rancidity of oils and fats pdf Dation of oils and fats denote that hydroperoxides are not the only compounds. Stansby, as early as 1943, showed that old rancid drying oils do Quality characteristics and oxidative stability of coconut oil during storage Diana Moigradean, MarianaAtena Poiana, Ioan Gogoasa Oxidative stability of oils is the resistance to oxidation during processing and storage [4. Oxidative stability is an important PDF The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of the 2 Alternative Forced Choice (2AFC) sensory method in detecting rancidity in soybean oils. Additionally, correlations between. rancidity oils fats pdf Rancidity is a term generally used to denote a condition of unpleasant odours and flavours in foods resulting from deterioration in the fat or oil. Rancidification, the product of which can be described as rancidity, is the. Rapid test for the detection of the rancidity of oils and fats Heike Kerwin, Kirsten Brunner, HeinzDieter Isengard There are different reasons for the going off of oils and fats: The oil can break down Oxidative rancidity [edit Oxidative rancidity is associated with the degradation by oxygen in the air. Via a free radical process, the double bonds of an unsaturated fatty acid can undergo cleavage, releasing volatile aldehydes and ketones. The Chemistry of Almond Quality Understanding Rancidity Development Alyson Mitchell PhD, Food Science Department, Rancidity is the unpalatable odor and flavor of deteriorating edible fats and oils in foods Rancidity occurs via two Although rancidity is one of the most pressing problems Oils can be particularly susceptible to rancidity because their chemistry which makes them susceptible to oxygen damage. When food scientists talk about rancidity, they are often talking about a specific type of rancidity involving oxygen damage to foods, and this type of rancidity is called oxidative rancidity. The application of the ferric thiocyanate method to the determination of incipient rancidity in fats and oils A. McFarlane Oil Soap 1943 20 (11). Fast detection of rancidity in potato crisps using enoses based on mass spectrometry or gas sensors crisps are fried in oils that contain a high amount of all silience to rancidity of oils, it has become a reference in the crisp industry. Measuring Rancidity in Fats and Oils Download as PDF File (. measuring Techniques review for Rancidity of Fats and Olis. Measuring Rancidity in Fats and Oils Two Types of Rancidity Selecting an optimum test for lipid oxidation is difficult due to the complexity of. and cosmetic formulation today, significantly comprise of fats and oils derived from natural plants. Lipids extracted from vegetable sources have limited stability upon storage. Fats start detoriating from the very moment; it is extracted from the vegetable or plant source. Abstract AOCS Official Method Cd 8b90(1)is a procedure for determination of peroxide value of fats and oils. As oxidation causes rancidity, or the quality deterioration of fats and oils, the Rancidity definition, having a rank, unpleasant, stale smell or taste, as through decomposition, especially of fats or oils: rancid butter. Oxidative rancidity is caused by oxidation in unsaturated oils or fats. When these types of oils or fats are exposed to oxidation, they begin decomposing into shortchain fatty acids, such as butyric acid, which gives the fats a rancid taste. Microbial Decomposition of Fats, Oils and Other Lipids Rancidity could also be as a result of microbial decomposition of fats, oils and other lipids. When these processes occur in food, undesirable odours and flavors can result. Microbial contamination of food such as edible oil is the most common health risk. PDF Rancidity and Antioxidants Tlcharger, bilization would be ideally based on a thorough knowledge of the inherent factors which make the nut meats susceptible or resistant to oxidative fat rancidity degrees of rancidity RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Oxygen absorptian The oxygen absorption of walnut pieces and the equivalent amount of walnut oil are shown Tech Tip Fats and Oils ChromaDex. Many factors can affect the tendency of an oil to become rancid. The first is too much exposure to air. Since oxidative rancidity is the most likely kind of rancidity to affect your food oils, you always want to keep those oils in bottles that are tightly capped. Autoxidation of Fats and Oils C. Dollear Products that contain fats and oils turn rancid and deteriorate in other ways when they arc exposed to air. The action known as autoxidation, imparts rancidity, and that for maximum sta \ C fats. PEROXIDE VALUE essential oils DEFINITION AND SCOPE The amount of peroxides of oils indicate the degree of primary oxidation and therefore its likeliness of becoming rancid. Tech Tip 0011 Fats and Oils analytics consulting ingredients standards What is the best way to measure rancidity in my sample? That is an often asked and simple question that. Rancidity is the complete or incomplete oxidation or hydrolysis of fats and oils when exposed to air, light, moisture or by bacterial action, resulting in unpleasant taste and odor. Chemistry teacher support material 1 Investiation 7 1 Investigating the Oxidative Rancidity of Polyunsaturated Oils Research Question How do different storage temperatures (20. 0 C) of sunflower oil affect FOOD FATS AND OILS Institute of Shortening and Edible Oils 1750 New York Avenue, NW, Suite 120 and Edible Oils, Inc. , 1750 New York Avenue, NW, Washington, DC, and rancidity and as sources of the essential nutrient vitamin E. The common types of tocopherols and tocotrienols A Food Science tidbite: To delay oxidative rancidity in your kitchen, purchase cooking oils in smaller containers (or portion out large bottles, and store excess in the fridge for later use), seal inuse bottles with a tightfitting cap, and store oils in a cupboard away from light and heat. All oils are fats, but not all fats are oils. They are very similar to each other in their chemical makeup, but what makes one an oil and another a fat is the percentage of hydrogen saturation in the fatty acids of which they are composed. CONTENTS Physical Oxidative rancidity. Oils containing highly unsaturated fatty acids are spontaneously oxidized by atmospheric oxygen at ordinary temperatures. The oxidation takes place slowly and results in the formation of short chain fatty acids (C 4 to C 10) and aldehydes which give a rancid taste and odour to Rancidity is a natural process affecting oils; however, understanding the process and how to test for levels of oxidative compounds can help purchasers and formulators ensure they select the highest quality oils for use in developing nutritional products. eventually produces rancidity in oil, with accompanying off flavours and smells. All oil is in a state of oxidation you cannot Oxidation of food grade oils Editor: Dr Matt Miller of less than 30 in marine oils but AV may need to be as low as 10, depending on the market. Hydrolytic Rancidity of Oils Offflavor development Decreases temperature at which frying oils begin to smoke (smoke point) Dealing with hydrolytic rancidity in oils Rancidity is a very general term and in its most general meaning, it refers to the spoilage of a food in such a way that it becomes undesirable (and usually unsafe) for consumption. Rancidity is a term generally used to denote unpleasant odours and flavours in foods resulting from deterioration in the fat or oil portion of a food. Three different mechanisms A) Technologically significant reactions (oleochemistry) 1. esterification enzymatic (lipases) B. Rancidity of oils and fats hydrolytic rancidity scented rancidity reversion propylgallate pure fats (oils) 12 0 20 40 60 80 100 Summary. The Wheeler test for peroxides proved to be relatively the most reliable method for the examination of olive oils for rancidity. The Issoglio test, although of no value for testing rancidity, can be of use in differentiating the natural olive oils from the refined olive oils. The oils that failed our tests had defects such as rancidity and many of these oils did not taste good, said Dan Flynn, executive director of the Olive Center at UC Davis. New Study Finds Consumers Paying a Premium Price for Cheap, Adulterated, Imported Olive Oil. Evaluation of Tests for Rancidity in Edible Packaged Oils JOHN E. Food Technology Department, Massachusetts State College PENTANE AND RANCIDITY IN OILS AND CHIPS763 Fig. 3Pentanedevelopment in the headspace gas ofpotato chips stored at 60C as measured by gas chromatography.
Related Images:
- Bad boys 1995 1080 dts
- Nurse jackie season 6 episode 11
- Frontline july 25
- Mujin Wakusei Survive 01
- Power 50 cent
- Ray harryhausen presents
- Alice chains 2018
- Drop the baby
- Savita episode 1
- Dugi wow guide
- After Dark Harmony 1 Jayne Castle
- Wonder Woman The Art And Making Of The Film
- Pc game serial crack
- Out of time lektor
- Enter of dragon
- Introduction To Digital Logic Design Pdf
- Viaggi di nozze
- A moving 12
- Remix new wave
- Pc ps2 games
- Tu meri video
- Street Child
- QMS Conversion A Process Approach
- Lin on the
- Heavy rock albums
- Telemann georg philipp
- Evil dead 2018 yify
- ZULU 2018 PUBLIC
- Yify 1080p robocop
- Breaking bad seasons 1 4
- Scooby doo
- Mind game 2018
- Satisfy a man
- Kenichi the mightiest disciple
- Dillon francis and dj snake get low
- BDSM Pain Gate Case 2
- 2000 Nissan Frontier Crank Pulley Timing Marks
- Die hard francais
- Teen mom 3 s01e07
- Once fallen nl
- Black white gf
- The day of the future past
- In another life
- Advanced Schutzhund
- Gameloft hd games
- An Einem Sonnabend Im Oktober
- Tomb raider chronicles
- World war z 1080p brrip x264 ac3 jyk
- Paragon Migrate OS to SSD
- Humko tumse pyaar hai
- Best of def leppard
- Plazma Burst Cheats Unblocked
- A chump at oxford
- Dans la maison french xvid
- Person of interest 720 s02e22
- The resident 2018
- Everybody backstreet boys
- The sucker punch
- Rise of the nor
- Body and beyond
- Bering sea gold the bitter end
- Beauty and the beast S02E09
- The first 48 bloody
- On turning away
- Love hate s2
- Downton abbey s04e06 nl subs
- Continuum s01e10 web
- The devils door 2018 hdrip
- Nashville s01e11 720p
- Tiffany star
- Les miserables dvdr
- How To Play Uno Spin
- Resignation Letter Due To Stress
- Comentario biblico pentecostal pdf
- Cisco aironet 1600 series access point data sheet
- Numara stelele
- Private Lesson Template
- Best of the manhattans
- Fix me swanky tunes
- Planet earth complete series 2018
- Seed Storage of Horticultural Crops
- Ashley wallbridge the inner me
- COSSACKS 3 KEYGEN